A recent research shows that AI models are facing a growing challenge of losing access to their online training data.
This trend of increasing restrictions may lead to models learning from limited, biased, and outdated information in the future.
The Data Provenance Initiative, an independent academic organization, carried out a comprehensive study that revealed a significant decline in web data accessibility for AI models.
The researchers examined robots.txt files and terms of use for 14,000 web domains that provide data for well-known AI training datasets such as C4, RefinedWeb, and Dolma.
Between April 2023 and April 2024, there was a noticeable increase in the percentage of tokens in these datasets that were completely blocked for AI crawlers, rising from approximately 1% to 5-7%.
Tokens refer to the individual sentence and word components utilized for training AI models. The rise was particularly striking for key data sources, with the proportion of blocked tokens increasing from less than 3% to 20-33%.
Researchers anticipate that this trend will persist in the upcoming months, with OpenAI experiencing the highest frequency of blocks, followed by Anthropic and Google.
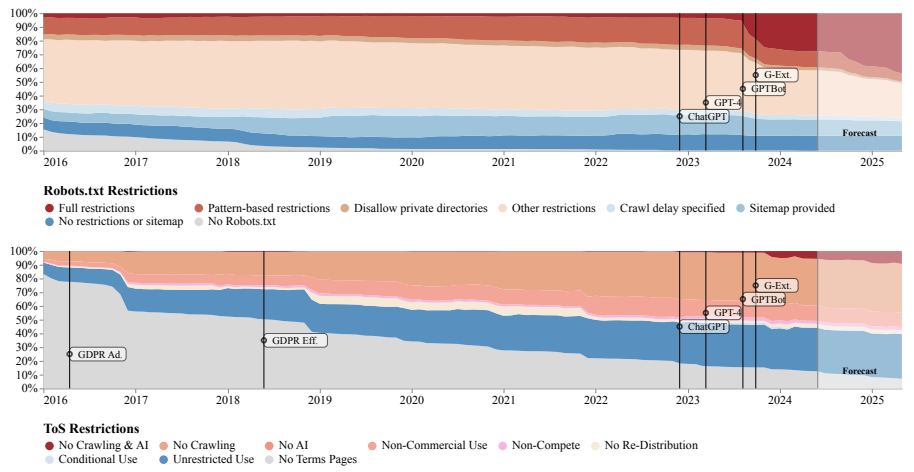
The primary sources that are implementing limitations are news websites, forums, and social media platforms. On news sites, the proportion of completely restricted elements increased significantly from 3% to 45% in just one year.
Consequently, there is likely to be a decrease in their presence in the training data in favor of corporate and e-commerce sites, which have fewer restrictions but often provide lower quality content.
This shift could have a particular impact on AI developers, as the industry has recognized that learning from high-quality data leads to the creation of superior models.
The research also brings attention to a mismatch between the actual usage of generative AI models and the content within their training data.
This could have implications in legal disputes where publishers take legal action against AI companies, alleging that services such as ChatGPT are in competition with their information offerings based on the content created by publishers.
This advancement may pose challenges in training effective and dependable AI systems, potentially increasing the cost of training.

However, high-quality content providers could benefit from new revenue streams. OpenAI and Meta CEO Mark Zuckerberg have expressed concerns about the impossibility or unaffordability of licensing all the necessary data for AI model training.
OpenAI has recently secured multi-million dollar deals with publishers to access their content for real-time display in chat systems and AI training, and other companies may also pursue similar agreements unless there are significant changes in fair use rulings.
Other Stories You May Like
