Intel introduced its newest artificial intelligence chip, Gaudi 3, in response to the increasing demand for semiconductors capable of training and deploying large AI models like OpenAI’s ChatGPT.
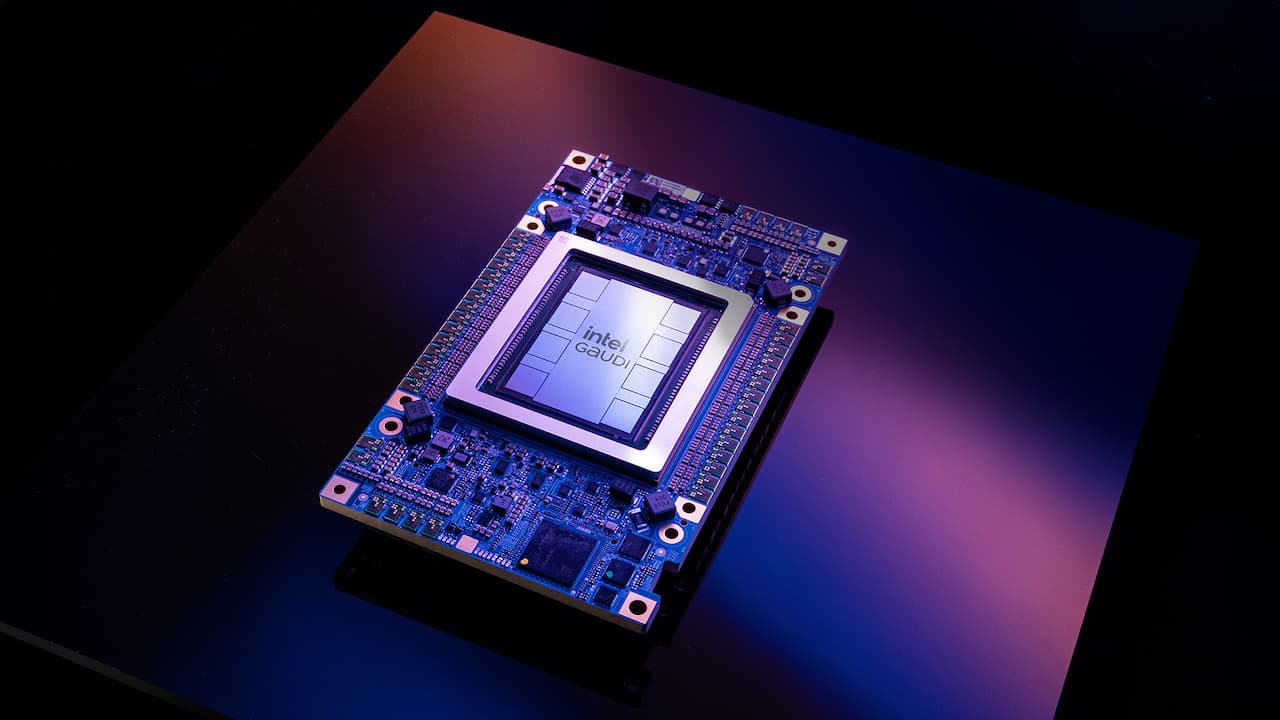
The Gaudi 3 chip has over twice the power efficiency and 1.5 times faster AI model processing compared to Nvidia’s H100 GPU.
This chip offers various configurations, including a bundle of eight chips on one motherboard and a card for existing systems.
Intel tested their Gaudi 3 chip on various models such as Meta’s open-source Llama and the Abu Dhabi-backed Falcon.
The chip demonstrated its capability to assist in both training and deploying models, including ones for speech recognition like Stable Diffusion and OpenAI’s Whisper model.
Intel claims that its chips consume less power compared to Nvidia’s offerings including Blackwell chips.
Nvidia dominates the AI chip market, holding approximately 80% share with its GPUs.
GPUs have been favored by AI developers for their high-performance capabilities over the last year.
Intel announced the availability of its new Gaudi 3 chips in the third quarter. Partners like Dell, Hewlett Packard Enterprise, and Supermicro will integrate these chips into their systems. The specific price range for Intel’s Gaudi 3 chips was not disclosed alongside the announcement.
Das Kamhout, Intel’s VP of Xeon software, predicts strong competition with Nvidia’s latest chips, emphasizing Intel’s competitive pricing and distinct features like an open integrated network on chip, utilizing industry-standard Ethernet. He believes Intel’s offering is robust and competitive.
The data center AI market is projected to expand alongside the growth of infrastructure for AI software deployment by cloud providers and businesses.
This growth indicates potential opportunities for other competitors in AI chip manufacturing, despite Nvidia’s current dominance in the market.
Running generative AI and purchasing Nvidia GPUs can incur high costs for companies. To mitigate expenses, businesses seek alternative suppliers to reduce financial burdens.
Nvidia’s stock has surged by over threefold in the past year due to the AI boom, reflecting its dominance in the market. In contrast, Intel’s stock has only risen by 18% during the same period.
AMD aims to broaden its market by offering more AI chips for server use, including its latest data center GPU, the MI300X. Notably, Meta and Microsoft are among its current clients.
Nvidia has unveiled its latest GPUs, the B100 and B200, successors to the H100, with enhanced performance. These new chips are anticipated to become available for shipping later this year.
Intel’s networking group, led by Sachin Katti, emphasizes collaboration within the software ecosystem to develop open reference software.
The focus is on creating building blocks that offer flexibility, enabling users to customize solutions rather than being constrained to pre-packaged ones.
This approach aims to empower users to assemble tailored solutions suiting their specific requirements, rather than being limited to purchasing predefined solutions.
Intel’s Gaudi 3 chip utilizes a powerful five-nanometer process, indicating the company’s collaboration with an external foundry for manufacturing.
Apart from Gaudi 3, Intel intends to produce AI chips, possibly for external firms, at a forthcoming Ohio factory slated for operation by 2027 or 2028, according to CEO Patrick Gelsinger’s recent statements to the press.
Related Stories:
